Introduction
Dans un environnement de vente au détail de plus en plus numérique, les étiquettes électroniques de rayon (ESL) représentent l’une des technologies les plus efficaces pour renforcer l’efficacité des magasins, améliorer l’expérience des clients et mettre en place des stratégies de prix dynamiques. Si le concept des étiquettes électroniques peut sembler simple – des étiquettes de prix numériques remplaçant les étiquettes traditionnelles en papier – les implications pour les leaders technologiques sont multiples et stratégiques. Ce guide est destiné aux directeurs des technologies (CTO) qui envisagent d’utiliser des étiquettes électroniques, avec une analyse approfondie des composants, des avantages, des défis et de l’impact quantitatif de la technologie sur les opérations de vente au détail.
Cet article aborde également l’intégration avec d’autres technologies en magasin, fournit des conseils pratiques de mise en œuvre et cite des données réelles pour étayer chaque point de vue.
Diagramme : Fonctionnement du système ESL
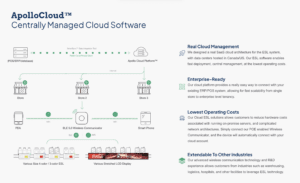
Ce diagramme fournit une représentation visuelle du fonctionnement d’un système ESL , y compris les interactions entre les étiquettes d’affichage, l’infrastructure de communication et le logiciel de gestion central.
1. Qu’est-ce qu’une étiquette électronique de rayonnage ?
Les étiquettes électroniques de rayon (ESL) sont des étiquettes numériques qui affichent des informations sur les produits dans les rayons des magasins, généralement à l’aide de la technologie e-ink ou LCD. Contrairement aux étiquettes en papier, les étiquettes électroniques peuvent être mises à jour à distance, ce qui permet une tarification dynamique, une plus grande précision et une réduction des coûts de main-d’œuvre. Les ESL peuvent être considérés comme une évolution de la technologie du commerce de détail, reliant les magasins physiques aux systèmes numériques de back-end.
Principaux éléments de l’ESL

- Technologie d’affichage : Les ESL utilisent principalement des écrans à encre électronique en raison de leur faible consommation d’énergie et de leur excellente visibilité dans diverses conditions d’éclairage. Des options LCD sont également disponibles pour les affichages nécessitant des couleurs ou des conceptions plus complexes.
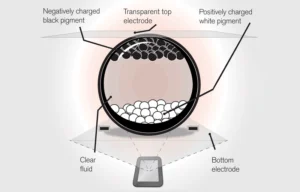
- Infrastructure de communication : Les ESL utilisent généralement la radiofréquence (RF) ou l’infrarouge (IR) pour communiquer, les technologies BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) et Wi-Fi apparaissant également comme des options viables. Parmi ces technologies, le BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) s’impose comme le meilleur protocole sans fil pour les ESL en raison de sa faible consommation d’énergie, de sa connectivité fiable et de sa capacité à gérer plusieurs connexions simultanément.L ‘efficacitéénergétique de BLEpermet aux ESL de conserver une longue durée de vie de la batterie tout en assurant des mises à jour en temps réel, ce qui en fait un choix idéal pour les environnements de vente au détail à grande échelle.

- Batterie et gestion de l’alimentation : La plupart des ESL fonctionnent à l’aide de piles rechargeables, qui peuvent durer entre 5 et 10 ans, en fonction de la fréquence des mises à jour, ce qui constitue une solution très rentable et une proposition de valeur à long terme.
2. Tendances du marché et taux d’adoption
Le marché ESL a connu une croissance significative en raison de la numérisation croissante des magasins de détail et des attentes des clients en matière de mise à jour des prix en temps réel. Le marché des ESL était évalué à environ 734 millions de dollars en 2020 et devrait atteindre 2,4 milliards de dollars d’ici 2026, avec un taux de croissance annuel moyen de 21,7 % [1]. L’adoption accélérée des ESL est attribuée aux grands détaillants qui recherchent des solutions évolutives pour lutter contre les pénuries de main-d’œuvre et la nécessité d’une synchronisation omnicanale.
Tendances en matière d’adoption
- Tendances géographiques : L’Europe est à la pointe de l’adoption de ESL , avec plus de 60 % des détaillants en épicerie qui déploient des systèmes ESL , en raison des coûts de main-d’œuvre élevés et de la pression réglementaire en faveur d’une tarification précise [2]. Aux États-Unis, l’adoption gagne du terrain, en particulier dans les grandes chaînes telles que Kroger et Walmart.
- Secteurs de la vente au détail : Les magasins d’alimentation représentent 45 % du déploiement de ESL , suivis par les magasins d’électronique (20 %) et les magasins de bricolage (15 %) [3]. Les détaillants en alimentation bénéficient considérablement de la tarification dynamique et de la réduction des erreurs.
3. Avantages de l’anglais langue seconde
3.1 Rapport coût-efficacité
L’un des principaux avantages des étiquettes électroniques est la réduction des coûts de main-d’œuvre. La tarification traditionnelle exige que les employés du magasin remplacent manuellement les étiquettes en papier, ce qui peut être à la fois coûteux en main-d’œuvre et source d’erreurs. Des études indiquent que les épiceries consacrent 200 à 300 heures par semaine à la mise à jour des prix [4]. La mise en place d’ESL peut réduire ce temps de 90 %, ce qui permet aux détaillants d’économiser environ 200 000 dollars par an pour un magasin de taille moyenne [5].
- Réduction du gaspillage de papier : Les ESL éliminent la nécessité d’imprimer fréquemment des étiquettes. On estime que chaque magasin utilisant les ESL peut économiser plus de 2 millions de feuilles de papier par an, contribuant ainsi à la réalisation des objectifs de développement durable.
3.2 Tarification dynamique
La tarification dynamique est une caractéristique essentielle du commerce de détail, qui permet de s’aligner sur les offres des concurrents, de réagir à la demande et d’optimiser les stocks. Les ESL permettent de modifier immédiatement les prix dans plusieurs magasins en cliquant sur un bouton. Une étude de cas de la Harvard Business Review a démontré que la tarification dynamique augmentait les marges bénéficiaires de 6 à 8 % dans les environnements de vente au détail grâce à une synchronisation plus efficace des promotions et à des ajustements de prix basés sur l’élasticité [6].
3.3 Amélioration de la précision des prix
Les erreurs de prix constituent un point sensible pour les détaillants. Des enquêtes suggèrent que 30 à 40 % des étiquettes de prix dans les magasins traditionnels sont obsolètes ou incorrectes à tout moment [7]. Les ESL permettent un contrôle centralisé des prix, garantissant que les mises à jour sont effectuées en temps réel dans tous les points de vente. Les risques de non-conformité sont ainsi atténués et la confiance des clients est renforcée.
3.4 Amélioration de l’expérience des clients
L’expérience client peut être grandement améliorée grâce aux ESL. Certains modèles de ESL sont dotés de fonctions interactives, telles que des codes QR permettant d’accéder à des informations détaillées sur les produits ou à des remises de fidélité. Des études ont montré que 70 % des clients sont plus enclins à s’intéresser aux produits dotés d’étiquettes de prix interactives [8]. Les ESL garantissent également que les remises annoncées correspondent aux prix en rayon, ce qui réduit l’insatisfaction des clients.
4. Défis liés à la mise en œuvre de ESL
4.1 Coût initial de l’investissement
Le coût initial des ESL peut être un facteur dissuasif important pour les détaillants. Le coût moyen d’un système ESL est de 8 à 12 dollars par étiquette. Pour un magasin ayant besoin de 20 000 étiquettes, cela se traduit par un investissement initial de 160 000 à 240 000 dollars, sans compter l’installation de l’infrastructure comme les passerelles de communication. Cependant, le retour sur investissement est généralement atteint en 1 à 2 ans, principalement grâce aux économies de main d’œuvre et à la réduction des erreurs [9].
4.2 Intégration aux systèmes existants
Les ESL doivent s’intégrer de manière transparente aux systèmes de gestion de la vente au détail (RMS), aux ERP et aux solutions de gestion des stocks afin de garantir un flux de données précis. Le développement de ces intégrations peut s’avérer complexe, en particulier pour les détaillants dotés d’anciens systèmes. Les directeurs techniques doivent travailler en étroite collaboration avec les fournisseurs de ESL pour garantir la compatibilité, la disponibilité des API et les protocoles de sécurité.
4.3 Gestion de la batterie
La durée de vie des piles est un élément crucial. Bien que de nombreux ESL revendiquent une durée de vie de 5 ans ou plus, cette durée dépend fortement de la fréquence de mise à jour des étiquettes. Si les prix changent plusieurs fois par jour, les piles s’épuisent plus rapidement. Un plan stratégique de remplacement ou de gestion des piles doit être envisagé.
4.4 Communication et interférence des signaux
Les ESL s’appuient sur un réseau de communication robuste. En fonction de la taille du magasin, les interférences et la force du signal peuvent devenir des défis, en particulier pour les étiquettes à radiofréquence. L’emplacement des passerelles de communication et des tests réguliers sont essentiels pour garantir des performances fiables.
5. Intégration avec d’autres technologies
5.1 Technologies de l’IdO et des magasins intelligents

Les ESL constituent un élément essentiel de l’écosystème IoT dans le commerce de détail. Lorsqu’ils sont intégrés à des caméras intelligentes et à des capteurs d’étagères, les ESL peuvent contribuer à une expérience transparente en magasin en permettant un suivi intelligent des stocks et même en établissant un lien avec l’analyse des clients pour déterminer comment les changements de prix influencent le comportement d’achat en temps réel.
5.2 RFID et gestion des stocks
Les ESL peuvent être intégrés à des étiquettes RFID pour un meilleur suivi des stocks. Cette combinaison permet d’avoir une vue d’ensemble en temps réel de la disponibilité des produits en magasin. Une étude a montré que les détaillants qui utilisent la RFID avec les ESL ont amélioré la précision de leur inventaire jusqu’à 99 %, contre 85 à 90 % pour les contrôles d’inventaire manuels [10].
5.3 Intégration des caisses automatiques et des téléphones portables
L’intégration avec les solutions de selfcheckout est une autre capacité clé des ESL. Des détaillants tels qu’Amazon Go ont exploité les ESL pour s’assurer que le prix que les clients voient en rayon est cohérent avec le prix à la caisse, afin d’éviter les divergences. En outre, les ESL dotés de la technologie BLE peuvent se connecter aux smartphones des clients pour leur envoyer des promotions personnalisées ou les aider à naviguer à l’intérieur du magasin. La technologie BLE permet une connexion fiable et économe en énergie, améliorant ainsi l’engagement des clients et l’efficacité opérationnelle.
6. Impact quantitatif des ASP
6.1 Économies de main-d’œuvre
- Gain de temps : Des études montrent que l’étiquetage manuel des prix prend environ 15 à 20 secondes par étiquette. Dans un magasin où 30 000 références changent de prix chaque semaine, les étiquettes ESL permettent d’économiser jusqu’à 150 heures par semaine.
- Réduction des coûts : Sur la base d’un salaire moyen de 15 dollars de l’heure, les ALS peuvent entraîner des économies de main-d’œuvre de 2 250 dollars par semaine, soit environ 117 000 dollars par an.
6.2 Impact de la tarification dynamique sur le chiffre d’affaires
- Optimisation de la démarque : Un projet pilote de Carrefour utilisant les ESL pour la gestion des démarques a montré une augmentation de 20 % des taux de vente des denrées périssables, tout en réduisant les déchets alimentaires de 18 % [11].
- Prix compétitifs : Les ASP permettent aux détaillants d’aligner leurs prix presque instantanément, ce qui se traduit par une augmentation des ventes pouvant aller jusqu’à 4 % dans les zones urbaines concurrentielles [12].
6.3 Mesures de durabilité
Les ESL contribuent de manière significative à la réduction de l’empreinte carbone d’un détaillant en minimisant l’utilisation du papier. Un magasin utilisant 30 000 étiquettes papier par mois génère 360 000 étiquettes par an, ce qui équivaut à environ 1,8 tonne d’ émissions de CO2. Les ESL, avec leur batterie d’une durée de vie de 5 à 10 ans, réduisent considérablement cet impact sur l’environnement [13].
7. Stratégies de mise en œuvre pour les CTO
7.1 Sélection des fournisseurs
Le choix du bon fournisseur est crucial pour une mise en œuvre réussie de ESL . Les directeurs techniques doivent évaluer les fournisseurs sur la base des critères suivants
- Durée de vie de la batterie et efficacité énergétique
- Capacités d’API et d’intégration
- Évolutivité et disponibilité de l’assistance dans plusieurs régions
- Modèles de tarification (par exemple, SaaS, CapEx)
- Assistance à la clientèle et offres de garantie
Les principaux fournisseurs du marché ESL sont ATI ApolloTechné, SES-imagotag et Pricer. Ces entreprises dominent collectivement environ 70 % du marché mondial ESL [14].
7.2 Programmes pilotes et déploiement progressif
Les directeurs techniques devraient envisager de lancer un programme pilote avant de procéder à une mise en œuvre à grande échelle. Les programmes pilotes permettent d’identifier les difficultés d’intégration et les problèmes de réseau, et fournissent des données sur le retour sur investissement dans le monde réel pour justifier une expansion ultérieure. Un déploiement progressif, en commençant par les départements à forte valeur ajoutée comme l’électronique ou les denrées périssables, peut offrir des gains et des enseignements rapides.
7.3 Intégration et sécurité des données
L’intégration avec les systèmes d’arrière-plan du magasin est primordiale. Les directeurs techniques doivent travailler en étroite collaboration avec les équipes informatiques et les équipes chargées des données pour s’en assurer :
- Synchronisation des données en temps réel: Veillez à ce que tous les systèmes de prix et d’inventaire soient synchronisés afin d’éviter les divergences.
- Sécurité des données: Les ASP fonctionnent sur des réseaux internes ; il est donc essentiel de garantir un cryptage de bout en bout. La mise en œuvre des protocoles SSL/TLS et la segmentation du réseau peuvent contribuer à la protection contre les cybermenaces.
8. L’avenir de l’anglais langue seconde : Tendances émergentes
8.1 Analyse avancée et IA
Les ESL modernes évoluent et intègrent des fonctions pilotées par l’IA. Ces étiquettes peuvent désormais collecter des données, telles que le temps d’attente et l’engagement des clients, afin de fournir des informations sur les performances des produits. Les algorithmes d’IA peuvent également aider à ajuster automatiquement les prix sur la base de modèles prédictifs liés à la demande, à la concurrence ou aux niveaux de stock.
8.2 Encre couleur et promotions numériques

La plupart des LEF sont aujourd’hui monochromes, mais l’encre électronique couleur devient de plus en plus abordable. Cette avancée permet de réaliser des promotions plus efficaces en magasin, en attirant l’attention des clients sur les réductions ou les articles à forte marge. On s’attend à ce que les LEP couleur représentent 15 à 20 % du marché d’ici à 2026 [15].
8.3 Intégration avec la robotique
Plusieurs détaillants étudient la possibilité d’utiliser des robots de mise en rayon qui interagissent avec les ASP. Ces robots, tels que ceux produits par Simbe Robotics, sont conçus pour vérifier les niveaux de stock en rayon et l’exactitude des étiquettes, automatisant ainsi une autre tâche à forte intensité de main-d’œuvre.
8.4 Blockchain pour la transparence de la chaîne d’approvisionnement
La technologie blockchain est également testée en conjonction avec les ESL pour offrir une plus grande transparence sur l’approvisionnement et l’authenticité des produits. Les clients peuvent scanner un code QR sur le site ESL pour voir l’historique complet de la chaîne d’approvisionnement du produit, une fonctionnalité particulièrement attrayante pour les consommateurs de la génération Z, qui privilégient la consommation éthique.
8.5 Écrans E-Ink grand format pour la signalisation traditionnelle
Les écrans e-ink grand format devraient être de plus en plus adoptés pour la signalisation traditionnelle, remplaçant les écrans LCD et les tableaux de menu LCD dans les restaurants à service rapide. Cette évolution est due à la faible consommation d’énergie de l’encre électronique, à l’excellente lisibilité dans diverses conditions d’éclairage et au coût de maintenance globalement réduit par rapport à la technologie LCD. La restauration rapide peut particulièrement bénéficier de cette transition en affichant des menus dynamiques et des contenus promotionnels avec une consommation d’énergie minimale.
9. Études de cas : Mise en œuvre réussie de ESL en Amérique du Nord
9.1 Mise en œuvre de ShopRite ESL en Pennsylvanie

ShopRite, une importante coopérative de supermarchés aux États-Unis, a entrepris un important déploiement ESL sur son site de Matamoras, en Pennsylvanie. En 2021, le magasin a intégré près de 40 000 ALS pour moderniser ses opérations. Cette initiative visait à numériser les fonctions du magasin et à rationaliser les processus d’étiquetage des prix. Les ESL, disponibles dans différentes formes et tailles, ont permis de répondre à la diversité de la gamme de produits du magasin, y compris les produits secs et humides. Cette transition a non seulement amélioré la précision des prix, mais a également permis au personnel de consacrer plus de temps au service à la clientèle et aux activités en magasin.
9.2 Le programme pilote d’étiquettes de prix numériques de Walmart
En 2022, Walmart a lancé un programme pilote pour évaluer l’efficacité des ESL dans certains magasins d’Amérique du Nord. Au bout d’un an, le programme a fait état d’une réduction de 9 % des coûts de main-d’œuvre liés aux changements de prix et d’une amélioration notable de la satisfaction des clients. Le projet pilote a également démontré une capacité accrue à concurrencer les détaillants en ligne en permettant une correspondance des prix en temps quasi réel.
9.3 La transition des détaillants en alimentation canadiens vers les ASP
Loblaw, un grand distributeur canadien de produits alimentaires, a étudié la possibilité de passer des étiquettes papier traditionnelles aux étiquettes électroniques. Le système existant ( ESL ) n’affichait que des informations sur les prix. Le détaillant a cherché à tirer parti des ESL en tant que point de contact vital pour le client en magasin, en y intégrant des données plus complètes. En partenariat avec RRD, Loblaw a développé un système qui fournit des étiquettes de produits complexes à la demande en utilisant une seule source de données. Cette transition a permis d’accroître considérablement la productivité et d’améliorer l’expérience d’achat globale.
Conclusion
Les étiquettes électroniques de rayonnage constituent une proposition convaincante pour les détaillants qui souhaitent moderniser leurs opérations, réduire les coûts de main-d’œuvre, améliorer la précision des prix et, en fin de compte, accroître la satisfaction des clients. Malgré les investissements initiaux et les difficultés d’intégration, les avantages quantifiables en termes d’économies de main-d’œuvre, d’augmentation des ventes grâce à une tarification dynamique et d’amélioration de la précision des stocks constituent un argument commercial de poids en faveur de l’adoption du site ESL .
Pour les directeurs techniques, une mise en œuvre réussie dépend de la sélection de la bonne technologie, de la gestion de l’intégration avec les systèmes existants et de la planification de l’évolutivité. Alors que le paysage de la vente au détail continue d’évoluer, les ASP seront sans aucun doute un élément central du magasin intelligent du futur, permettant une prise de décision en temps réel, basée sur des données, et améliorant l’expérience d’achat dans son ensemble.
Références
- Market Research Future. « Electronic Shelf Label Market Analysis, 2020-2026 . » https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/electronic-shelf-label-market-6875
- Rapport d’analyse du commerce de détail européen, 2022. « ESL Tendances d’adoption en Europe. »
- Statista. « ESL Pénétration par secteur de vente au détail, 2023 . » https://www.statista.com
- Retail Management Insights. « Coûts de main-d’œuvre dans la gestion des prix, 2021 ».
- Gartner. « Analyse de la rentabilité des étiquettes électroniques de rayonnage, 2022 ».
- Harvard Business Review. « Stratégies de tarification dynamique dans le commerce de détail, 2020 ».
- Retail Dive. « Le coût réel des erreurs de tarification, 2019 ».
- Nielsen. « Engagement des consommateurs envers les étiquettes numériques, 2021 ».
- ESL Aperçu du marché par Grand View Research, 2022.
- RFID Journal. « Impact de la RFID sur la précision des inventaires, 2021 ».
- Étude de cas de Carrefour sur les ASP, 2020.
- KPMG Retail Analytics Report, 2022.
- Rapport d’impact environnemental. « Réduction de l’empreinte carbone par l’adoption du site ESL , 2021 ».
- MarketWatch. « Top Vendors in the ESL Market, 2023 ».
- Future Market Insights. « Croissance de l’encre couleur dans le commerce de détail, 2023 ».
Prochaines étapes
Pour explorer les avantages que les ALS peuvent apporter à votre commerce de détail ou pour planifier une consultation, communiquez avec notre équipe dès aujourd’hui. Nous nous engageons à vous aider à transformer vos opérations en magasin et à profiter des avantages de cette technologie novatrice. Nos experts peuvent fournir une évaluation personnalisée de vos besoins et vous guider tout au long du processus de mise en œuvre, en veillant à ce que vous tiriez le meilleur parti de votre investissement dans les ALS. Laissez-nous vous aider à franchir la prochaine étape vers des opérations de vente au détail plus intelligentes et plus efficaces.